-
Lab. Research Contents (研究内容)
-
- The research goal of our lab is to Create New Value based on human sensing.
- Sensing targets include Biosignals, Human motion, Eye movements, and Human-to-human or device output sensing etc.
-
-
Keywords (キーワード)
- Body motion measurement;
- Eye-tracking;
- Empirical mode decomposition;
- Deep learning;
- Driver Characteristics Analysis;
- Human behaviors analysis;
- Human-computer interaction (HCI);
- Agricultural work support;
- Vehicle Driving;
- Usercentered design.
-
Student Research
A Walk-through Type Authentication System Design via Gaze Detection and Color Recognition
Based on the using of glasses type eye-tracking device, in this study we focused on the detection of user’s eye movement and tried to propose a walk-through type of authentication system design by color recognition. Through a set of preparatory experiments, we tested the usability of the designed system, and found the effect of light setting on the accuracy of the experiment.
Mask Recognition via AR Smart Glasses
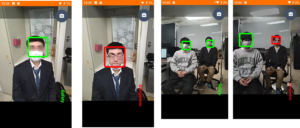
A Smart Glasses-based Gesture Recognition and Translation System for Sign Languages
Analyzing the Effects of Driving Experience on Backing Maneuvers Based on Data Collected by Eye-Tracking Devices
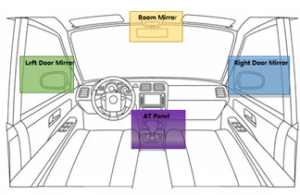
This study aims to analyze the impact of driving experience on backing maneuvers by utilizing data collected from eye-tracking devices. A comparative analysis is conducted between novice and experienced drivers to investigate differences in gaze patterns and fixation positions during backing maneuvers. Real-time gaze data is collected using eye-tracking devices during backing maneuvers.

The findings reveal distinct disparities in gaze behavior and fixation positions between novice and experienced drivers. Novice drivers have cluttered vision and tend to focus more on the right door mirror and switch their eyes back and forth between the two areas of interest.
A Deep Learning-driven Aerial Dialing PIN Code Input Authentication System via Personal Hand Features
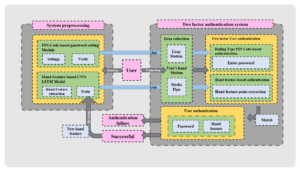

Based on the using of “Leap motion” device and “Media pipe” solutions, in this paper, we try to propose a new two-factor dialing type input authentication system powered by aerial hand motions and features without contact. To be specific, based on the design of the aerial dialing system part, as the first authentication part, we constructed a total of two types of hand motion input sub systems using Leap motion and Media Pipe, separately. The results of FRR (False Rejection Rate) and FAR (False Acceptance Rate) experiments of two sub systems show that the Media Pipe one is more comprehensive and superior in terms of applicability, accuracy, and speed. Moreover, as the second authentication part, the user’s hand features (e.g., proportional characteristics associated with fingers and palm) were used for specialized CNN-LSTM model training, and finally obtained a satisfactory accuracy.
An Eye movements-based Sketch Drawing Process Analysis and Experience Prediction via BiLSTM-KAN Deep Learning Model
According to design and apply a set of experiments, we focus on analyzing the eye movement data of the subjects in the sketch of imaginary object shapes and compare the differences in the sketch between the experienced painters and the novice. Specifically, we used Tobii Pro Glasses 3 eye tracker to record 49 groups of 16 painters with different experience, and performed Mann-Whitney U test. The analysis results of Mann-Whitney U test show that the novice’s eyes tend to be left and down on the whole, their eyes are scattered, and their focus on the central position of the picture is not concentrated and sustained. In the classification model built based on Bi-LSTM and Critical attention network (KAN), Val Loss, Accuracy and F1 score are 0.0305, 0.90 and 0.8845 respectively. It shows that the model has good classification performance and generalization ability when dealing with unbalanced data.
A Smart Glasses-based Real-time Micro-expressions Recognition System via Deep Neural Network

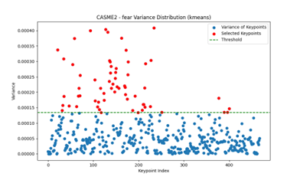
In this study, a new micro-expression recognition method, K-Means clustering algorithm neural network (K-net), was proposed to select key face landmarks based on motion variance and K-Means clustering algorithm and capture the dynamic changing features of expressions combined with LSTM. Specifically, we used MediaPipe’s Face Mesh to extract key face landmarks from CASME, CASME II, and SAMM datasets. Then the motion variance of each key face landmark is calculated, and the key face landmarks with the largest motion amplitude are selected by K-Means clustering algorithm. By selecting these key face landmarks, not only the feature dimension can be significantly reduced without compromising the accuracy, but also the feature information most closely related to micro-expression recognition can be retained. The experimental results show that the proposed method has an overall accuracy of 85.96%, especially in the recognition of fear, surprise and sadness. At the same time, in order to verify the effectiveness of the method, compared with traditional methods (such as LBP-TOP), the results show that the accuracy of the model is improved by about 22%, and significant performance improvement is achieved. .
A Cloud-based Sign Language Translation System via CNN with Smart Glasses
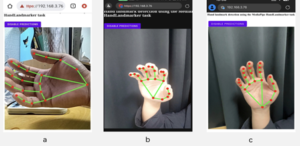
in this paper, a sign language translation system for smart devices based on browser/server architecture is developed. When a hearing-impaired person gestures in front of the user who is using a smart device with our proposed system (e.g., smart glasses with camera), their sign language gestures can be translates into text by MediaPipe with a TensorFlow’s 1D-CNN model, and then uses the natural language processing library named “compromise” for lexical annotation. Based on this library, the gestures can be arranged in order according to their lexical properties and displayed on the screen of the smart device screen, which facilitates barrier-free communication between hearingimpaired people who are unfamiliar with sign language and ordinary people. Unlike previous studies that used YOLOv5 for target detection, this study uses MediaPipe to identify gesture bone keypoints. This method not only improves the accuracy through keypoint recognition, but also reduces the requirement of device performance. At the same time, the software supports multiple smart device GPU operations, which improves translation performance. In the testing phase, we invited 10 testers to test the whole model completely, and the final average accuracy reached 85%..
A Real-time Recognition Gait Framework for Personal Authentication via Image-Based Neural Network: Accelerated by Feature Reduction in Time and Frequency Domains
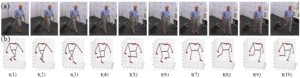
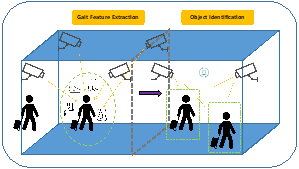
In this paper, we proposed an innovative real-time MediaPipe-based gait analysis framework and a new Composite Filter Feature Selection (CFFS) method via key nodes, angles, lengths calculating. Then, based on the proposed method, we extract the aimed features as a new dataset and verified it by 1D-CNN neural network. Furthermore, we also applied Hilbert-Huang transform to investigate these extracted gait features in the frequency domain, improving the performance of our proposed framework to achieve real-time under higher recognition accuracy. The experimental results show that the innovative gait recognition framework and data processing technology can reduce the gait feature data, speed up the process of gait recognition, and still maintain the original recognition accuracy.
